One of the most common mistakes with independent clauses is joining them without correct punctuation. This error is called a run‐on sentence. An independent clause standing alone should end in a period, question mark, or exclamation mark.
Joining independent clauses
If you want to join independent clauses, you should use a semicolon, or use a comma plus a coordinating conjunction. Using a comma without a conjunction is not sufficient.
He drove off in the Mercedes, Erica watched him go. (incorrect)
The previous example is a comma splice, a punctuation error that causes a run‐on sentence. A comma alone cannot join independent clauses.
He drove off in the Mercedes. Erica watched him go. (correct)
Here, the independent clauses are separate sentences. Each ends correctly with a period.
He drove off in the Mercedes; Erica watched him go. (correct)
The two independent clauses are correctly joined with a semicolon.
He drove off in the Mercedes, and Erica watched him go. (correct)
The two independent clauses are correctly joined with a coordinating conjunction ( and) preceded by a comma.
Run-ons with conjunctive (sentence) adverbs
Watch out for another kind of run‐on sentence. Some words look like coordinating conjunctions but aren't. These words cannot be used to join independent clauses with a comma. Remember that the only time you can join independent clauses with a comma and not be guilty of a run‐on sentence is when one of the seven coordinating conjunctions ( and, but, for, nor, or, so, yet) follows the comma.
The impostors—words that look like coordinating conjunctions but are actually adverbs—are called conjunctive adverbs or sentence adverbs. The use of a comma to join a clause beginning with one of these words is common. But no matter how widespread the practice, it still creates a run‐on, and most teachers and editors won't accept it. Table 1 shows a few of the words to watch out for.
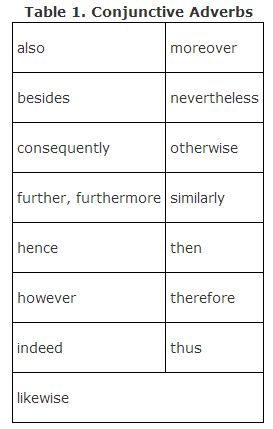
Some transitional phrases pose the same problem—for example, as a result, even so, for example, in other words, and on the contrary. Remember the rule that independent clauses can be joined with a comma only when the comma is followed by one of the seven coordinating conjunctions.
Scientists were convinced by the evidence; however, the Food and Drug Administration was slow to respond.
NOT Scientists were convinced by the evidence, however, the Food and Drug Administration was slow to respond.
The hurricane damaged the arena. Nevertheless, the game was played on schedule.
NOT The hurricane damaged the arena, nevertheless, the game was played on schedule.
Folic acid appears to exert a protective effect. For example, one study showed that it cut the rate of neural tube defects by two-thirds.
NOT Folic acid appears to exert a protective effect, for example, one study showed that it cut the rate of neural tube defects by two-thirds.
Run‐on sentences such as those described above are basic errors. On rare occasions, joining independent clauses with only a comma may be acceptable—for example, when the clauses are very short and have the same form, when the tone is informal and conversational, or when you feel the sentence rhythm calls for it.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Live by the sword, die by the sword.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
They smiled, they touched, they kissed.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I hardly recognized her, she was so thin. (The word “because” is understood here.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
You must have a good reason for writing an intentional run‐on sentence.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|