SETI—The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
Philosophical questions aside, what is the likelihood of finding another intelligent civilization? An answer lies in a number of factors, which have been expressed in the Drake Equation, an estimation of the fraction of stars with planets that harbor intelligent life. These factors include the fraction of stars that have planets, an estimation of which planets would have habitable conditions, and so forth: These are summarized in Table with some indication of the pessimistic and optimistic estimations of the numerical values assigned to each factor. Currently, these factors are mostly guesses because sound scientific evidence to produce reliable numbers does not exist. (Note that as an alternative, the Drake Equation can be expressed slightly differently as a product involving the stellar birthrate function and the life span of civilizations):
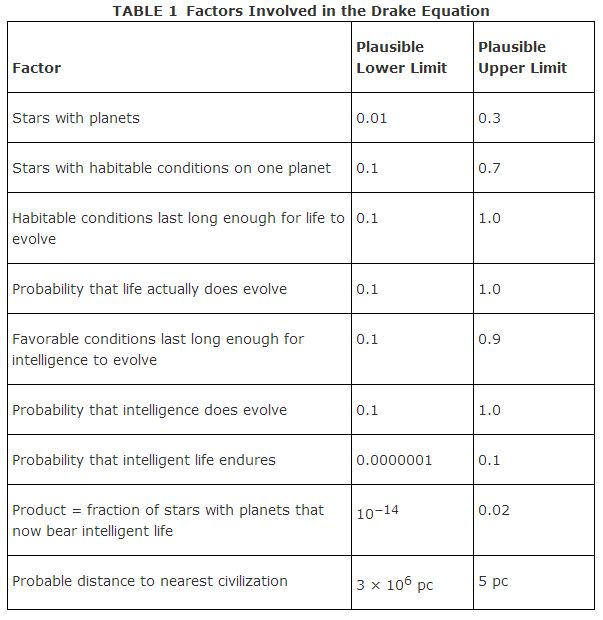
Expressed in a different fashion, the pessimistic point of view suggests that intelligent life is extremely rare, with one civilization present in every 1,000 galaxies. On the other hand, the optimistic viewpoint is that there exists an intelligent civilization for every 50 stars in the Galaxy. Until significant advances are made in understanding planetary occurrence as well as evolution of biological organisms, these two limits cannot be narrowed.
One other matter should be mentioned: Fermi's Question, “Where are they?” The late Italian physicist Enrico Fermi simply pointed out that assuming a civilization has reached the technological ability to explore space, and further assuming that they will, then the Galaxy must have already been explored. Present human technology would allow expansion out into the Galaxy at a velocity of approximately 100 km/s, equivalent to a travel distance of 1 pc in 10,000 years. This is too slow for human beings to travel to nearby stars, but spacecraft could be sent and discoveries returned (slowly) to Earth by radio communication.
Present technology could support construction of a sophisticated exploring system, a von Neumann machine, which would not only explore another solar system, but at arrival would first search out construction materials (in an asteroid belt) and energy sources (solar energy; hydrocarbons from atmospheres of gas giant planets) to replicate itself, sending the next generation of exploring spacecraft to other stars. Under these circumstances, the time to cross the Galaxy is approximately 300,000,000 years, an extremely short time compared to the actual age of the Galaxy (and even shorter if advanced technological discovery would allow travel at much higher velocities). It could be argued that civilizations choose not to explore or perhaps do not survive long enough to move outward into the Galaxy. Even so, it would take only one civilization to do so to leave evidence of its visitation in the solar system. Yet there is no evidence that the solar system ever has been visited now or in the past (in particular, no report of an unidentified flying object has ever been confirmed as an extraterrestrial visitation).
Given the above uncertainties and the expense of space exploration, the detection of radio signals from other civilizations has been the chosen approach for SETI, the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. The first effort in SETI occurred in 1960: Project Ozma involved 400 hours of radio telescope observation of two nearby solar‐type stars. Since then, there have been several dozen other projects, but none with a positive detection. Projects have included all sky searches in specific wavelength regions of the radio spectrum as well as searches paying specific attention to a selected sample of stars, for example, solar‐type stars. SETI investigation is also piggy‐backed upon other radio astronomical research by analyzing these signals to detect any form of artificial pattern superimposed upon the background of natural radio radiation coming from natural radio sources.
While SETI is a very small part of all astronomical investigation, the motivation for continuing the search is strong. New technology has greatly improved the sensitivity of radio receivers, making detection of ever weaker signals possible. Astronomical revision of ideas concerning stellar and planetary formation and especially the ability to detect the existence of planets suggest that habitable planets are more likely than once thought. Similarly, there are occurring major revisions of ideas concerning the origin and development of life.
At the same time, humanity has both deliberately and accidentally signaled its existence. After its refurbishment in the early 1970s, the Arecibo radio telescope was used to send a radio signal toward the globular cluster M13. Any civilization living in or near its million stars might receive that signal in about 13,000 years, if it has a radio telescope tuned to the correct frequency pointing in the direction of Earth. The Pioneer 10 spacecraft, which left the solar system, carries a plaque with schematics showing the solar system, human beings, and the position of the Sun in the Galaxy. Voyager 2 carries a phonograph record with classical and rock music, human conversation, and other artificial and natural sounds. This record also was encoded with information to reproduce pictures of typical earth scenes.